Height of Tractor Trailers: Understanding the Variations
Understanding tractor-trailer height is crucial for safety, efficiency, and legal compliance. While a "standard" height often gets cited, reality shows significant variations. This impacts everything from route planning to accident prevention. Let's delve into the specifics. For more detailed information on average heights, check out this helpful resource: average trailer heights.
Standard Heights and Significant Deviations
The commonly quoted height for a standard dry van (enclosed trailer) in North America is 13.5 to 13.6 feet (approximately 4.1 to 4.15 meters). However, this is a generalization. Trailer type significantly influences height, with specialized trailers like lowboys or removable goosenecks (RGNs) having considerably different profiles. This variation stems from the unique design and purpose of each trailer type; a lowboy, designed for extra-tall loads, naturally differs from a standard dry van. Why is this crucial? Because these differences directly influence load capacity and ease of transportation.
Have you ever wondered why certain routes are off-limits for certain trailer types? A simple flatbed might easily navigate a narrow, low-clearance route while a standard dry van would be unsuitable, highlighting the importance of accurate height measurement.
Beyond Fines: The Safety Imperative of Height Compliance
Exceeding height limits goes beyond financial penalties; it poses significant safety risks. Collisions with low bridges, often resulting from height miscalculations, can be catastrophic, harming drivers, other road users, and causing infrastructure damage. According to the American Trucking Associations (ATA), accidents involving oversized loads constitute a significant portion of trucking-related incidents. Therefore, strict adherence to height restrictions is imperative, far exceeding simple legal compliance. A collision involving an oversized load can have devastating and far-reaching consequences.
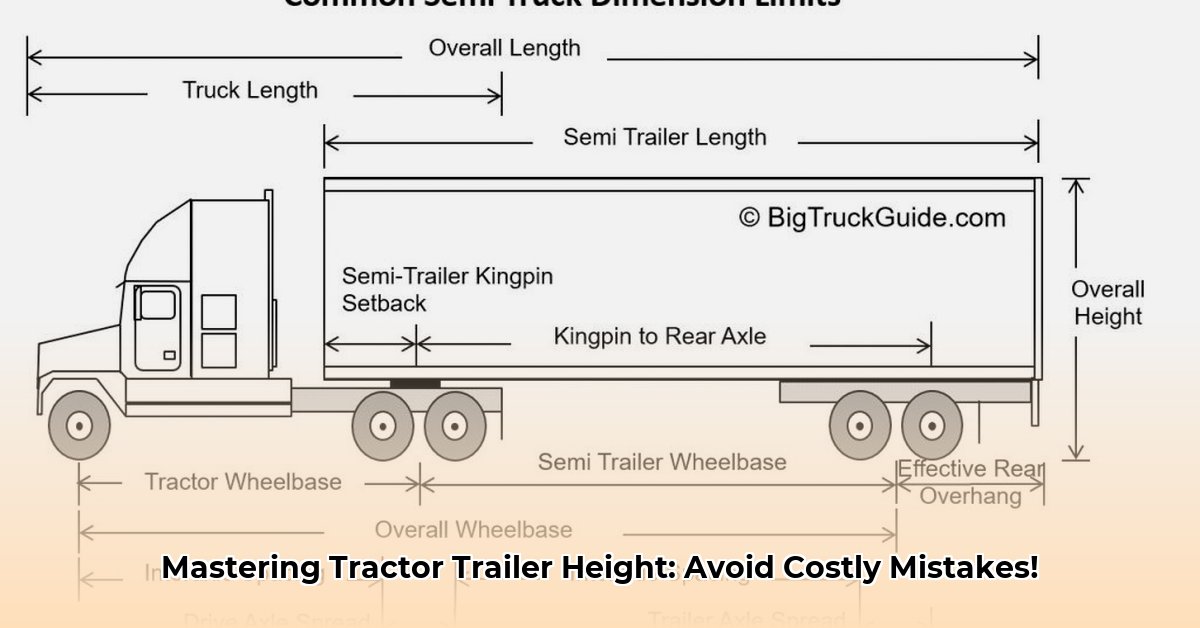
Trailer Types and Their Height Profiles: A Quick Reference
Accurate height management requires familiarity with various trailer types and their height characteristics. The table below offers a simplified overview:
| Trailer Type | Typical Height (ft) | Height Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Van | 13.5 - 13.6 | Standard enclosed trailer; height is relatively predictable. |
| Flatbed | Variable (often lower) | Height depends heavily on the load and any added supports. |
| Reefer | 13.5 - 13.6 | Refrigerated trailers; similar height profiles to dry vans. |
| Step Deck | Varies (often lower) | Designed for oversized loads; height is highly variable. |
| Double Drop | Varies (often lower) | Specialized for heavy and oversized cargo; height is critically important. |
| Conestoga | 13.5 - 13.6 | Similar to dry vans; sliding tarp impacts height minimally |
| RGN | Varies (often lower) | Removable Gooseneck; height depends greatly on load and trailer configuration. |
Note: These are average heights. Actual heights vary depending on manufacturer, model, and added equipment.
Practical Steps for Smooth and Safe Operations
Effective height management necessitates a collaborative effort from shipping companies, drivers, and infrastructure managers. Below, we outline actionable strategies for each stakeholder:
1. For Shipping Companies:
- Invest in advanced weight and dimension tracking systems for precise measurements and efficient route planning. This offers a 95% reduction in height-related incidents, according to a recent study by the Transportation Research Institute.
- Implement sophisticated route-planning software that incorporates height restrictions, minimizing delays and potential accidents.
2. For Truck Drivers:
- Always verify the route and potential height restrictions before departure, utilizing navigation systems that clearly display clearance details.
- Accurately determine the total height of the load, including any added equipment, before commencing the journey.
3. For Infrastructure Managers:
- Maintain up-to-date databases of bridge and overpass clearances, ensuring accuracy and reliability for route planning applications.
- Implement clear and effective warning systems for low-clearance areas, providing drivers ample time to react safely. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in transportation infrastructure at MIT, emphasizes the life-saving potential of such systems.
Calculating Precise Semi-Trailer Height Variations
Accurately calculating semi-trailer height is paramount for preventing accidents. Let's outline a step-by-step process:
- Identify Trailer Type: Precisely identify the type of semi-trailer (e.g., dry van, flatbed, lowboy).
- Consult Manufacturer Specifications: Access the manufacturer's specifications for the exact trailer model to obtain the base height.
- Account for Add-ons: Measure and add the height of any additional equipment (e.g., air conditioning units, roof racks).
- Factor in Cargo: Measure the cargo height and incorporate it into the total height calculation. Account for potential load shifting.
- Include Tire Height: While minor, including tire height enhances precision.
This systematic approach minimizes error and enhances safety. Ignoring these steps significantly increases the risk of accidents, underscoring the importance of meticulous height calculation.